Understanding sentence structure in English grammar is one of the most important steps in learning English. If you know how sentences are built, you can speak more clearly, write with confidence, and avoid common mistakes.
This guide is written for beginner to intermediate learners. We’ll use simple language, real-life examples, and clear explanations—just like a friendly teacher would. By the end, you’ll understand how English sentences work and how to build them correctly.
Sorry Generator
What Is Sentence Structure in English Grammar?
Sentence structure means the order of words in a sentence. It shows how different parts—like the subject, verb, and object—fit together to make meaning.
In English, word order is very important. Changing the order can change the meaning or make the sentence incorrect.
Basic idea:
Who does what (and to whom)?
Example:
- ✅ She reads a book.
- ❌ Reads she a book. (wrong order)
Why Sentence Structure Is Important
Good sentence structure helps you:
- Speak clearly and naturally
- Write correct emails, essays, and messages
- Avoid confusion and misunderstandings
- Sound more fluent and confident
Even if your vocabulary is good, wrong sentence structure can confuse listeners or readers.
The Basic English Sentence Structure (SVO)
The most common sentence structure in English grammar is:
Subject + Verb + Object (SVO)
Example:
- I (subject) eat (verb) breakfast (object).
- They play football.
- She likes music.
📌 Tip: Most English sentences follow this order.
Parts of a Sentence Explained Simply
Let’s break down the main parts of a sentence.
1. Subject
The subject tells us who or what does the action.
Examples:
- I work here.
- The teacher explains the lesson.
- My friends are waiting.
2. Verb
The verb shows the action or state.
Examples:
- run, eat, study, sleep
- is, am, are, was, were
Example:
- She is happy.
- They play chess.
3. Object
The object receives the action.
Examples:
- She reads a book.
- He bought a car.
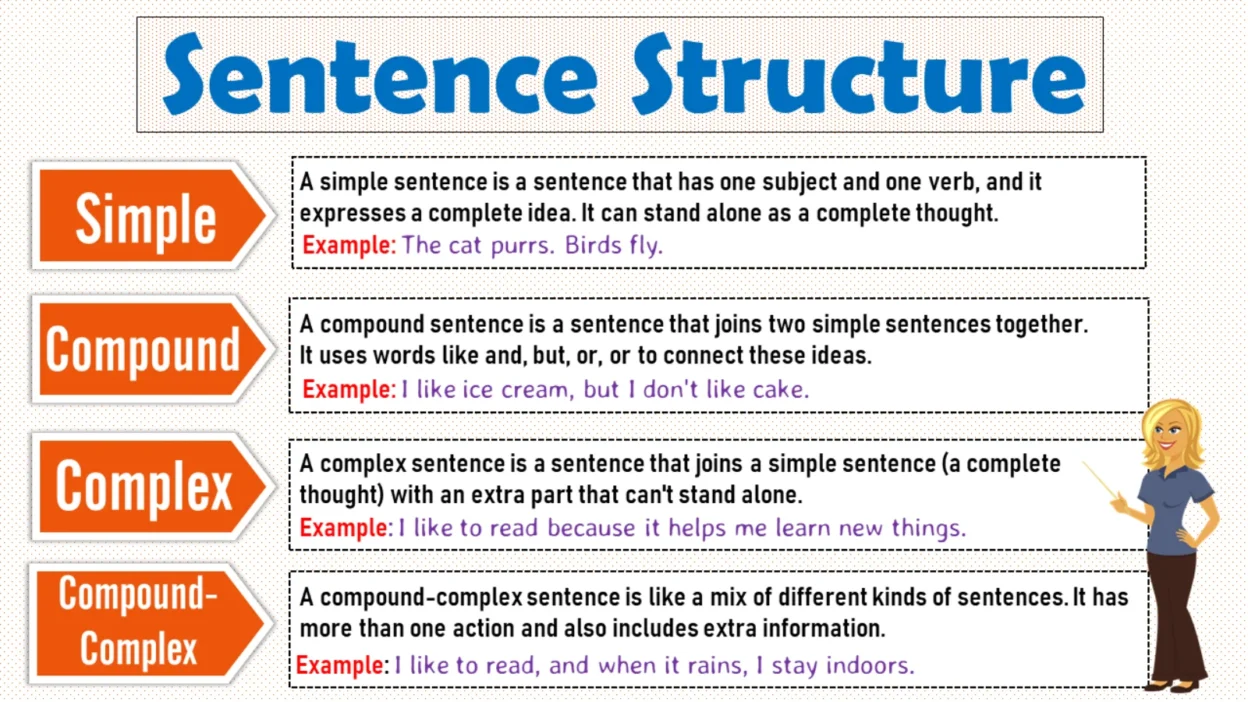
Simple Sentence Structure (One Independent Clause)
A simple sentence has:
- One subject
- One main verb
- A complete idea
Examples:
- I study English.
- She works at a hospital.
- We live in Canada.
Real-life use:
I’m tired.
The bus is late.
Sentence Structure with Adjectives and Adverbs
You can add more information to sentences using adjectives and adverbs.
Adjectives (describe nouns)
Adjectives usually come before the noun.
Examples:
- a big house
- an interesting movie
Sentence:
- She bought a new phone.
Adverbs (describe verbs)
Adverbs often come after the verb or at the end.
Examples:
- quickly, slowly, well, yesterday
Sentence:
- He speaks English well.
- We arrived early.
Negative Sentence Structure in English
To make negative sentences, we often use do not (don’t) or does not (doesn’t).
Structure:
Subject + do/does + not + base verb
Examples:
- I do not like coffee.
- She does not work here.
- They don’t understand the question.
⚠️ Common mistake:
- ❌ She doesn’t likes coffee
- ✅ She doesn’t like coffee
Question Sentence Structure in English
English questions have a different word order.
Yes/No Questions
Auxiliary verb + subject + main verb?
Examples:
- Do you like pizza?
- Does she live here?
- Are they ready?
Wh- Questions
Wh-word + auxiliary verb + subject + main verb?
Examples:
- Where do you live?
- What does he do?
- Why are they late?
Compound Sentence Structure
A compound sentence joins two simple sentences using a conjunction.
Common conjunctions:
- and
- but
- so
- or
Structure:
Independent clause + conjunction + independent clause
Examples:
- I wanted to go, but it was raining.
- She studied hard, so she passed the exam.
Complex Sentence Structure (Beginner-Friendly)
A complex sentence has:
- One main clause
- One dependent clause
Common words:
- because
- when
- if
- although
- while
Examples:
- I stayed home because it was cold.
- She called me when she arrived.
Sentence Structure with Time and Place
In English, time and place usually come at the end of the sentence.
Order:
Subject + Verb + Object + Place + Time
Example:
- I met her at the café yesterday.
- They study at home every evening.
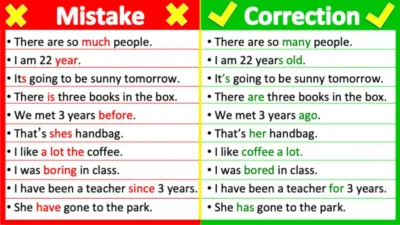
Common Sentence Structure Mistakes (and Fixes)
1. Wrong Word Order
- ❌ Very I like English.
- ✅ I like English very much.
2. Missing Verb
- ❌ She very happy.
- ✅ She is very happy.
3. Double Subjects
- ❌ My brother he works here.
- ✅ My brother works here.
Sentence Structure Examples for Practice
Correct the sentences:
- She don’t like tea.
- Yesterday I went store.
- He is play football.
Answers:
- She doesn’t like tea.
- Yesterday, I went to the store.
- He is playing football.
Sentence Structure Table (Quick Reference)
| Sentence Type | Structure Example |
| Simple | I eat lunch. |
| Negative | I do not eat meat. |
| Question | Do you eat meat? |
| Compound | I was tired, but I worked. |
| Complex | I stayed home because it rained. |
FAQ: Sentence Structure in English Grammar (People Also Ask)
What is sentence structure in English grammar?
Sentence structure is the way words are ordered to form correct and meaningful sentences in English.
What is the basic sentence structure in English?
The basic structure is Subject + Verb + Object (SVO).
Why is English sentence structure important?
It helps you communicate clearly, avoid mistakes, and sound natural in English.
How can I improve my sentence structure?
Practice writing short sentences, read simple English texts, and learn common patterns like SVO.
Is English sentence structure difficult?
No. Once you understand the basic rules, English sentence structure becomes much easier.
Key Takeaways: Sentence Structure Made Simple
- English usually follows Subject + Verb + Object
- Word order is very important
- Start with simple sentences, then move to longer ones
- Practice with real-life examples
- Learn common mistakes and avoid them
Final Thoughts & Practice Tip
Learning sentence structure in English grammar is like learning the foundation of a house. Once it’s strong, everything else becomes easier—speaking, writing, and understanding English.