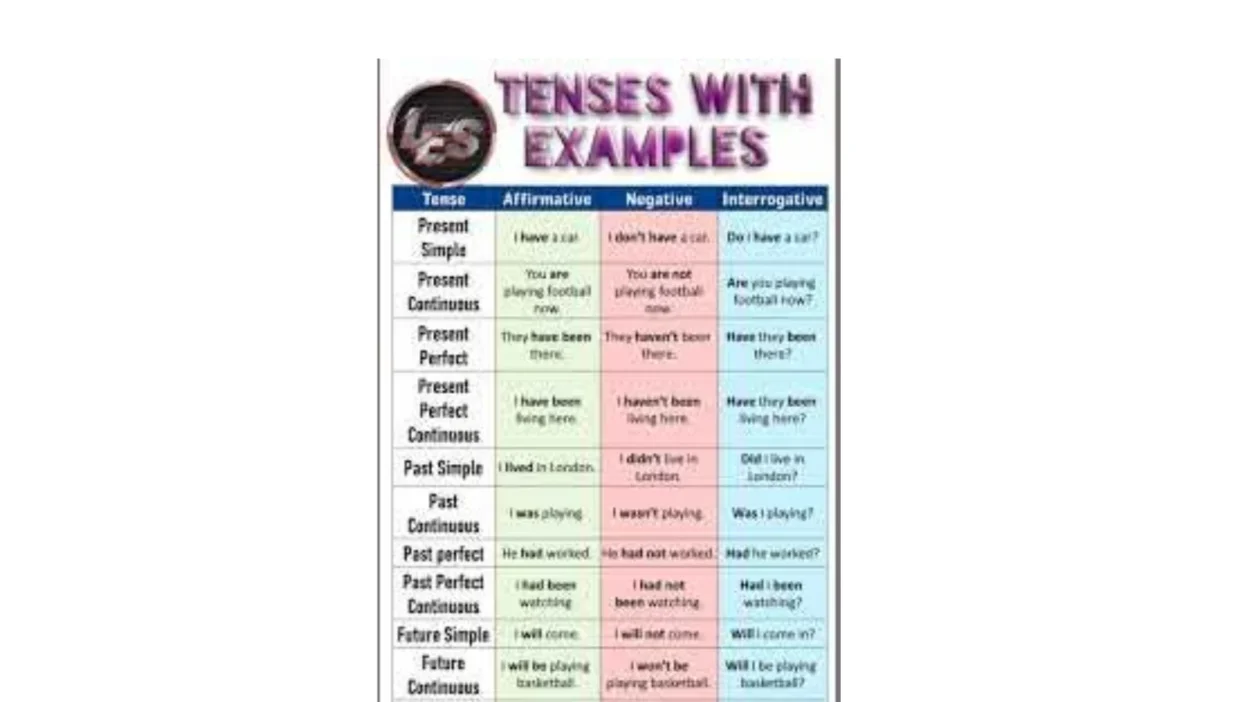
Understanding tenses in English grammar with examples is one of the most important steps in learning English. Tenses help us talk about time — what happened in the past, what is happening now, and what will happen in the future.
If English grammar feels confusing, don’t worry. In this guide, you will learn English grammar in simple words, with clear explanations, real-life examples, tables, and common mistakes to avoid. This article is perfect for beginner to intermediate learners.
Let’s start from the basics and build your confidence step by step. 😊
Sorry Generator
What Are Tenses in English Grammar?
In English grammar, a tense shows when an action happens.
👉 Every tense tells us:
- Time (past, present, or future)
- Action or state
- Duration or completion
Simple Example:
- I eat breakfast at 8 AM. (Present)
- I ate breakfast yesterday. (Past)
- I will eat breakfast tomorrow. (Future)
There are 12 main tenses in English, divided into three time categories.
Three Main Types of Tenses
| Time | Meaning |
| Present Tense | Actions happening now or regularly |
| Past Tense | Actions that already happened |
| Future Tense | Actions that will happen |
Each time has four forms:
- Simple
- Continuous
- Perfect
- Perfect Continuous
Present Tenses in English Grammar
1. Simple Present Tense
When to Use
- Daily habits
- General facts
- Timetables
- Permanent situations
Structure
Subject + base verb (+ s/es for he/she/it)
Examples
- I wake up early.
- She works in an office.
- Water boils at 100°C.
Common Mistakes
❌ She work hard
✅ She works hard
2. Present Continuous Tense
When to Use
- Actions happening right now
- Temporary actions
- Future plans (informal)
Structure
Subject + am/is/are + verb + ing
Examples
- I am studying English now.
- They are watching TV.
- She is meeting her friend tonight.
Common Mistakes
❌ I am study English
✅ I am studying English
3. Present Perfect Tense
When to Use
- Actions with no specific time
- Life experiences
- Recently completed actions
Structure
Subject + has/have + past participle
Examples
- I have finished my homework.
- She has visited London.
- We have never tried sushi.
Common Mistakes
❌ I have finish my work
✅ I have finished my work
4. Present Perfect Continuous Tense
When to Use
- Actions that started in the past and continue now
- Focus on duration
Structure
Subject + has/have been + verb + ing
Examples
- I have been learning English for 2 years.
- She has been working all day.
Past Tenses in English Grammar
5. Simple Past Tense
When to Use
- Actions completed in the past
- Specific time mentioned
Structure
Subject + past form of verb
Examples
- I watched a movie yesterday.
- She went to school.
- We played football last Sunday.
Common Mistakes
❌ I go to school yesterday
✅ I went to school yesterday
6. Past Continuous Tense
When to Use
- Action in progress in the past
- Interrupted actions
Structure
Subject + was/were + verb + ing
Examples
- I was sleeping when you called.
- They were playing outside.
7. Past Perfect Tense
When to Use
- An action completed before another past action
Structure
Subject + had + past participle
Examples
- I had eaten before he arrived.
- She had finished her work.
8. Past Perfect Continuous Tense
When to Use
- Duration before another past action
Structure
Subject + had been + verb + ing
Examples
- I had been waiting for an hour.
- They had been studying all night.
Future Tenses in English Grammar
9. Simple Future Tense
When to Use
- Decisions made at the moment
- Promises
- Predictions
Structure
Subject + will + base verb
Examples
- I will help you.
- She will call later.
- It will rain tomorrow.
10. Future Continuous Tense
When to Use
- Action in progress at a future time
Structure
Subject + will be + verb + ing
Examples
- I will be working at 9 AM.
- They will be traveling tomorrow.
11. Future Perfect Tense
When to Use
- Action completed before a future time
Structure
Subject + will have + past participle
Examples
- I will have finished by evening.
- She will have left before noon.
12. Future Perfect Continuous Tense
When to Use
- Duration up to a future time
Structure
Subject + will have been + verb + ing
Examples
- I will have been studying for 5 hours.
- They will have been living here for years.
Complete Tense Summary Table
| Tense | Example |
| Simple Present | I eat rice |
| Present Continuous | I am eating rice |
| Present Perfect | I have eaten rice |
| Present Perfect Continuous | I have been eating rice |
| Simple Past | I ate rice |
| Past Continuous | I was eating rice |
| Past Perfect | I had eaten rice |
| Past Perfect Continuous | I had been eating rice |
| Simple Future | I will eat rice |
| Future Continuous | I will be eating rice |
| Future Perfect | I will have eaten rice |
| Future Perfect Continuous | I will have been eating rice |
Practice Sentences (Try Yourself)
Fill in the blanks:
- She ___ (study) English every day.
- They ___ (watch) TV when I arrived.
- I ___ (finish) my work already.
- We ___ (travel) tomorrow morning.
👉 Practice daily to master English grammar easily.
Common Tense Mistakes Learners Make
- Mixing present and past tenses
- Forgetting -s / -es in simple present
- Using wrong verb forms
- Overusing future tense with “will”
💡 Tip: Focus on time words like yesterday, now, already, tomorrow.
FAQ: Tenses in English Grammar (People Also Ask)
What are tenses in English grammar?
Tenses show the time of an action — past, present, or future.
How many tenses are there in English?
There are 12 main tenses in English grammar.
Which tense should beginners learn first?
Start with Simple Present, Simple Past, and Simple Future.
Is English grammar hard to learn?
No. With simple explanations and regular practice, it becomes easy.
How can I practice English tenses daily?
Read, speak, write short sentences, and correct your mistakes.
Key Takeaways
- Tenses explain time and action
- English has 12 main tenses
- Learn step by step — don’t rush
- Practice real-life examples
- Focus on English grammar in simple words
Final Thought
Learning tenses in English grammar with examples may feel challenging at first, but it becomes easy when you understand the idea of time behind each tense. You don’t need to memorize all 12 tenses at once. Start with simple ones, use them in real-life sentences, and practice a little every day.